Transforming bladder cancer treatment: The rise of immunotherapy in community oncology practices
By IntrinsiQ Specialty Solutions
This is a retrospective cohort study using records from the Nucleus® inventory management database, which contains data from community oncology practices within the ION network. Patients diagnosed with bladder carcinoma, starting a line of drug therapy between December 2021 and November 2024, were identified (n=9,230). Patient starts were counted only in the month they first began their line of therapy (LOT). Shares of starts were calculated over time. Duration of first line of therapy (LOT 1) and the time to initiation of second line of therapy (LOT 2) were compared between patients on ICI and other regimens. Medians and 95% confidence intervals were reported using Kaplan-Meier estimates, along with log rank p-values.
Community Oncology Adopts Immunotherapy as a Standard of Care in First-line Bladder Cancer
The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) as LOT 1 for treatment of bladder cancer grew substantially at community oncology practices within the ION network over the last three years, growing from 32% in December 2021 to 45% in November 2024 (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Immunotherapy Share of LOT 1 Starts
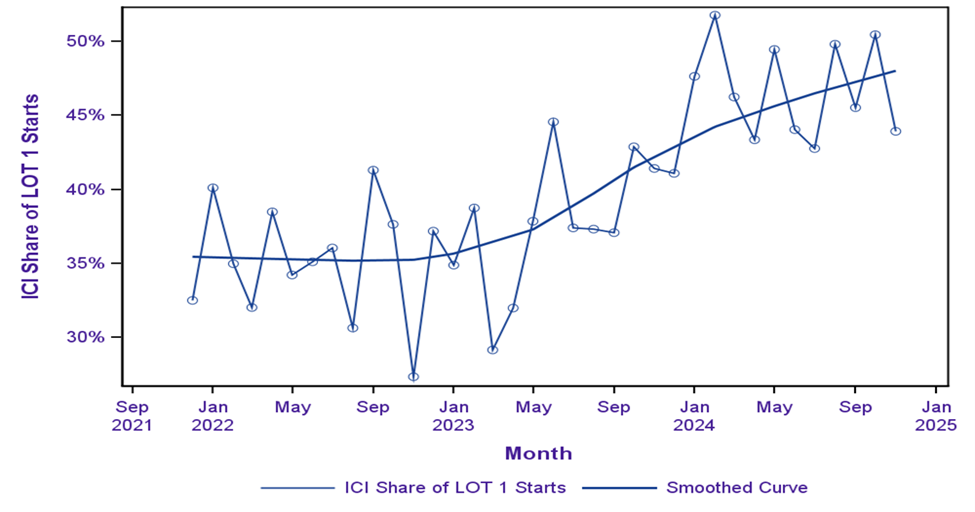
This increase was largely driven by use of the enfortumab vedotin-ejfv – pembrolizumab combination (Figure 2).
With initial FDA approval in April 2023 for patients who were platinum ineligiblei followed by expansion to all first-line metastatic patientsii in December 2023, the enfortumab vedotin-ejfv – pembrolizumab combination share of LOT 1 starts grew rapidly to 26% by November 2024 (Figure 2). This also corresponds with a decline in other ICI therapies over the same period.
The share of pembrolizumab monotherapy in LOT 1 starts has experienced a significant decline, decreasing from 18% in December 2021 to 10% in November 2024. Platinum-based therapy followed by maintenance avelumab has seen a complete drop in its share, declining from 6% in December 2021 to negligible use by November 2024. Atezolizumab monotherapy LOT 1 starts, reached a peak of 6% in June 2022 before falling similarly in 2024.
Figure 2. LOT 1 Immunotherapy Regimen Starts
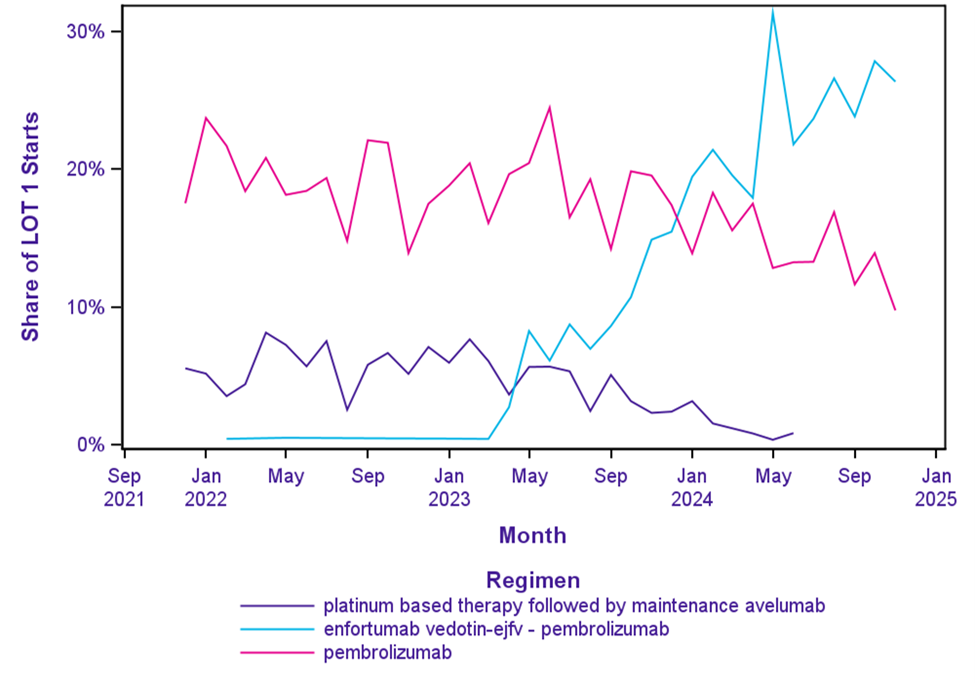
Note: Nominal use of nivolumab monotherapy and atezolizumab monotherapy are not displayed.
Immunotherapy Affords Longer Duration of LOT 1 and Longer Time to Next Treatment
We observed significant differences in both the duration of LOT 1 therapy and the time to initiation of LOT 2 therapy between patients receiving ICI therapy and those receiving other treatment modalities, suggesting the potential impact of ICI therapy in this patient population.
The median duration of LOT 1 for patients receiving ICI therapy was 5.4 months (95% CI, 5.1-5.8), significantly longer than the median duration of 1.7 months (95% CI, 1.7-1.9) observed in patients receiving other therapies. The interval from the initiation of LOT 1 to the commencement of LOT 2 was also significantly longer in patients treated with ICI therapy. The median time for this cohort was 28.5 months (95% CI, 23.4-33.9) compared to 7.5 months (95% CI, 7.2-7.8) for those receiving other therapies.
Community Oncology Responds Rapidly to EV-302 Trial Results
Emerging evidence suggests a notable trend of switching patients from pembrolizumab monotherapy to the combination of enfortumab vedotin-ejfv with pembrolizumab following release of the EV-302 trial data and subsequent FDA approval of the combination in April 2023.
In the second quarter of 2023, among patients initiating this combination therapy, 8% had completed a prior line of pembrolizumab monotherapy within two months (Figure 3). That share remained between 7% and 8% for the first three quarters post-FDA approval before starting to decline.
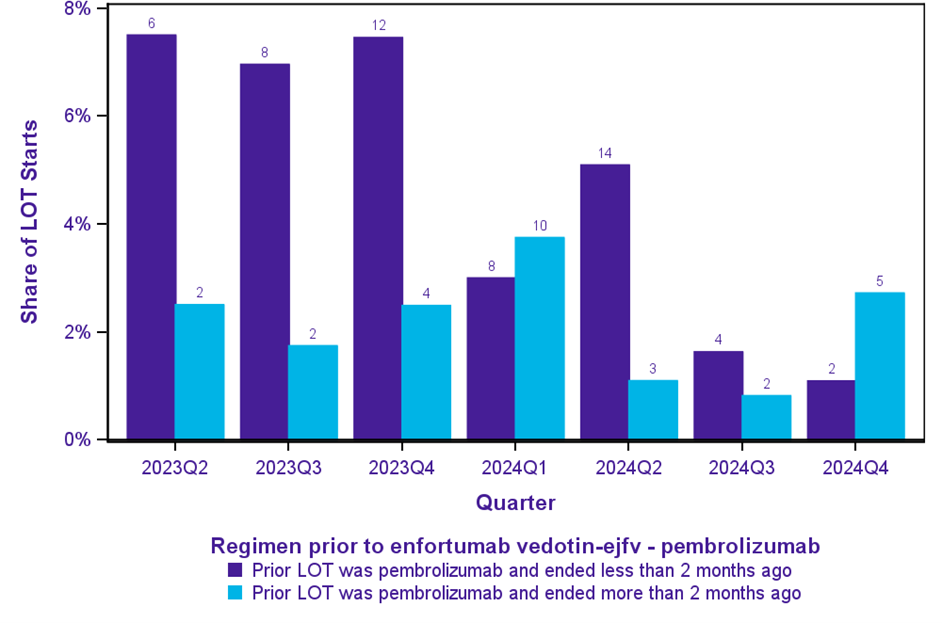
Note: Quarters before 2023 are not displayed. The last quarter only includes 2 months. Bars are labeled with raw counts. Denominator is enfortumab vedotin-ejfv – pembrolizumab starts.
Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of antibody conjugates with immunotherapy, specifically pembrolizumab with enfortumab vedotiniii . This study suggests community oncologists embraced the paradigm-shifting data presented at European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) for treatment of bladder carcinoma.



